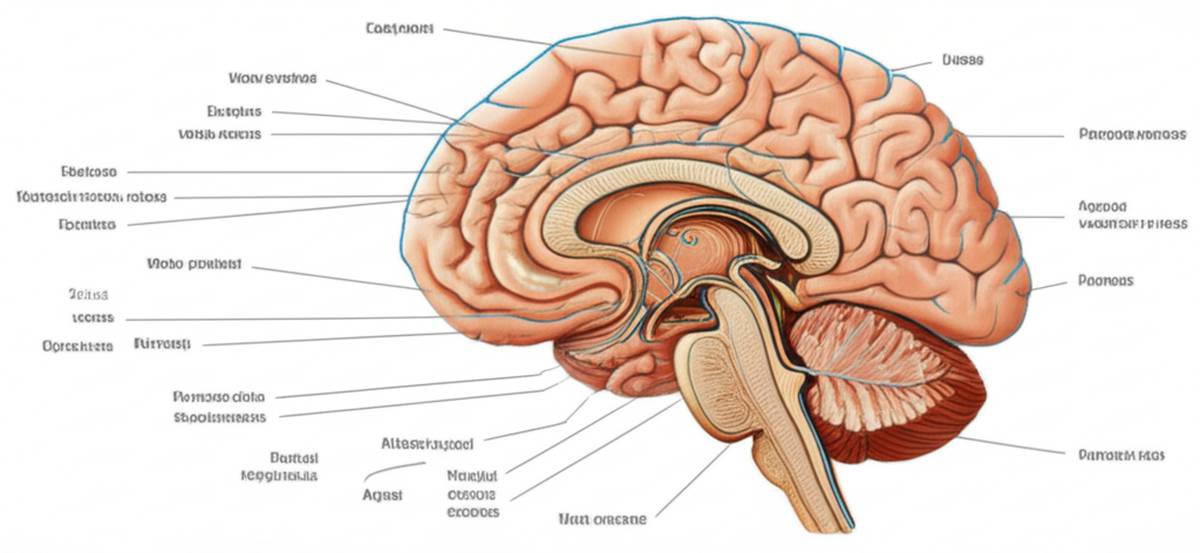
Understanding White Matter and Its Role in Your Body
Ever wondered what makes up the intricate wiring of your brain? One key component is white matter! This fascinating tissue plays a crucial role in how your brain communicates with the rest of your body. Let’s dive into what white matter is, how it functions, and why it’s so important for your overall health and well-being.
What is White Matter?
White matter is one of the two main types of tissue found in the brain and spinal cord. The other type is grey matter. White matter gets its name from its whitish appearance, which is due to the presence of a fatty substance called myelin. Myelin surrounds the nerve fibers (axons) and acts like insulation, speeding up the transmission of electrical signals between nerve cells.
The Composition of White Matter
- Myelinated Axons: The core component of white matter, axons are the long, slender projections of nerve cells that transmit electrical signals. The myelin sheath surrounding these axons is crucial for efficient communication.
- Oligodendrocytes: These are specialized glial cells that produce myelin in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord).
- Other Glial Cells: Besides oligodendrocytes, white matter also contains other glial cells like astrocytes and microglia, which support and protect nerve cells.
Functions of White Matter
White matter serves as the communication network of the brain, enabling different regions to connect and coordinate their activities. Some key functions include:
- Signal Transmission: White matter facilitates the rapid transmission of electrical signals throughout the brain and spinal cord. This is essential for everything from sensory perception to motor control.
- Connectivity: It connects different areas of grey matter, allowing them to work together and process information effectively.
- Learning and Memory: White matter plays a role in learning and memory by strengthening connections between brain regions.
White Matter and the Human Body: How It Connects Everything
So, how does white matter directly impact the human body? Think of it as the superhighway for information. Here’s a closer look:
Motor Control
White matter tracts connect the motor cortex (responsible for voluntary movement) to the spinal cord and muscles. Damage to these tracts can result in weakness, paralysis, or difficulty coordinating movements.
Sensory Perception
Sensory information from all over the body travels through white matter pathways to the brain for processing. This includes touch, temperature, pain, vision, hearing, and taste. Problems with these pathways can lead to sensory deficits or altered perceptions.
Cognitive Functions
White matter integrity is crucial for cognitive functions such as attention, memory, and executive function. Disruption of white matter networks can contribute to cognitive decline and neurological disorders.
Emotional Regulation
White matter connects brain regions involved in emotional processing, such as the amygdala and prefrontal cortex. These connections allow for the regulation of emotions and appropriate behavioral responses.
Factors Affecting White Matter Health
Several factors can influence the health and integrity of white matter. These include:
- Age: White matter naturally changes with age, with some decline in volume and integrity.
- Genetics: Genetic factors can influence white matter structure and function.
- Lifestyle: Lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and smoking can impact white matter health. A healthy diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants can support brain health. Regular exercise promotes blood flow to the brain and protects against white matter damage. Avoiding smoking is crucial, as smoking can impair blood flow and damage white matter.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as multiple sclerosis, stroke, and traumatic brain injury, can directly damage white matter.
Learn more about brain health on Wikipedia.
Maintaining White Matter Health
While some factors affecting white matter health are beyond our control, there are several steps you can take to support and maintain the health of your brain’s white matter throughout your life:
- Eat a Healthy Diet: Focus on consuming foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamins.
- Exercise Regularly: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Manage Stress: Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Get Enough Sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep per night.
- Engage in Cognitive Activities: Challenge your brain with puzzles, reading, learning new skills, and social interaction.
- Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Both can harm white matter.
- Consider exploring other resources on our blog for additional insights on brain health.
- Discover more strategies to enhance your overall well-being on our start here page.
- Learn about ways to improve your cognitive function on our wealth page.

The Future of White Matter Research
Research on white matter is ongoing, with scientists constantly learning more about its structure, function, and role in various neurological and psychiatric disorders. Advanced imaging techniques, such as diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), allow researchers to visualize and measure white matter integrity in vivo. This has led to a better understanding of how white matter is affected by disease and how it responds to treatment.
FAQs About White Matter
What happens if white matter is damaged?
Damage to white matter can result in a wide range of symptoms depending on the location and extent of the damage. Common symptoms include motor deficits (weakness, paralysis, incoordination), sensory deficits (numbness, tingling, pain), cognitive impairment (memory problems, attention deficits), and emotional disturbances.
Can white matter be repaired?
The brain has some capacity to repair and regenerate white matter, but the extent of recovery depends on the cause and severity of the damage. Rehabilitation therapies, such as physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy, can help improve function and promote recovery. Research is also exploring potential treatments to enhance white matter repair, such as stem cell therapy and pharmacological interventions.
How is white matter disease diagnosed?
White matter disease is typically diagnosed using brain imaging techniques such as MRI. MRI can visualize white matter lesions (areas of damage) and assess the overall integrity of white matter. Neurological examination and cognitive testing can also help determine the extent and nature of any functional deficits.
Understanding white matter and its role in your body is a great step toward prioritizing brain health. By adopting a healthy lifestyle and staying informed, you can support the health of your white matter and promote overall well-being. Remember that a proactive approach to brain health can have a significant impact on your quality of life!